Oral Presentation The Annual Scientific Meeting of the Endocrine Society of Australia and the Society for Reproductive Biology 2014
Thyroiditis related to cancer biological therapy: CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade (#117)
Introduction:
New immunomodulatory therapies for malignancies such as melanoma have transformed their management with significantly enhanced survival outcomes1. Antibodies against CTLA-4 (ipilimumab) and the programmed death-1 (PD-1) molecule increase the cytotoxic function of T-cells with excellent tumour response rates1,2 However, these therapies may also result in immune-related adverse effects. We describe 4 patients who developed thyroiditis due to CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade.
Case Series:
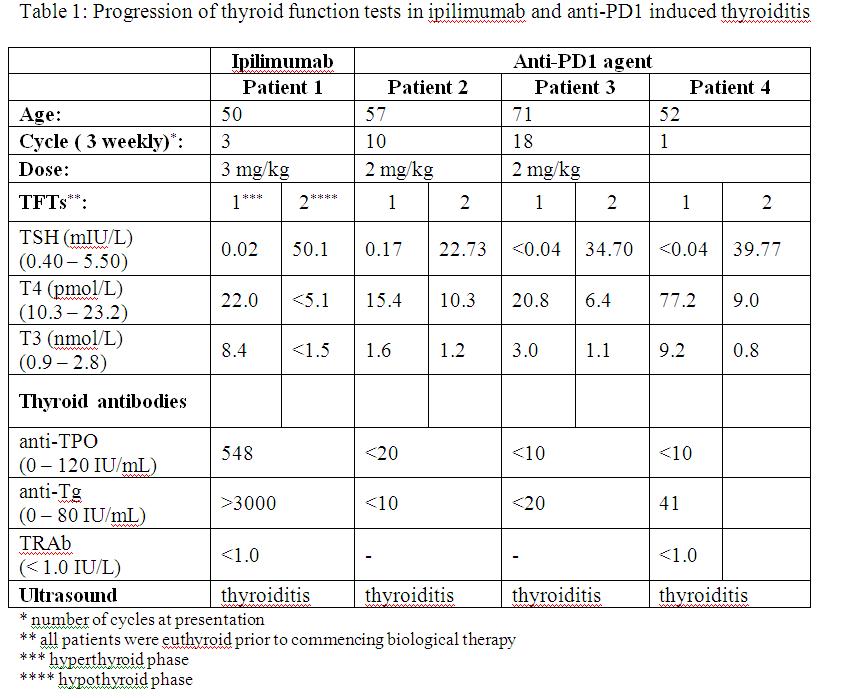
Patient 1 had a background of metastatic melanoma and received ipilimumab. Following 3 cycles of ipilimumab, he developed hyperthyroidism which progressed to hypothyroidism 4 weeks later (table 1). Findings on ultrasound were consistent with thyroiditis. Thyroid antibodies were present and levothyroxine replacement was also required.
Discussion:
Three patients received anti-PD-1 therapy with pembrolizumab (formerly MK3475) as part of the KEYNOTE-001 study, 2 of whom had metastatic melanoma and 1 non-small cell lung cancer. Two patients presented with hypothyroidism 9 – 12 months after commencing pembrolizumab (table 1), preceded by subclinical hyperthyroidism 4 months prior to presentation. The third patient received pembrolizumab at a dose of 10mg/kg and presented with hyperthyroidism after 1 cycle, progressing to hypothyroidism after 4 weeks. In all 3 patients, thyroid antibodies were not detected, but ultrasound findings were consistent with thyroiditis. One patient had a thyroid nodule and underwent fine needle aspiration. Cytology demonstrated benign follicular cells with several multinucleated giant cells. Two patients remain on levothyroxine replacement.
Thyroiditis is a known side effect of both CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade. CTLA-4 gene polymorphisms are associated with autoimmune thyroid diseases3. The exact mechanisms of anti-PD-1 induced thyroiditis remain unclear, but may be due to a switching of the immune system to an effector T-cell response, resulting in macrophage activation by interferon gamma, and cell-mediated thyroid damage4. Monitoring of thyroid function tests are required with use of these therapies.
- Hamid, O et al. Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in melanoma. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2013;369:134-144
- McDermott, DF et al. PD-1 as a potential target in cancer therapy. Cancer Medicine. 2013;2(5):662-673
- Min, L et al. Thyroid autoimmunity and ophthalmopathy related to melanoma biological therapy. European Journal of Endocrinology. 2011;164:303-307
- Tomer, Y et al. Interferon induced thyroiditis. Best practice and research clinical endocrinology and metabolism. 2009;23:703-712